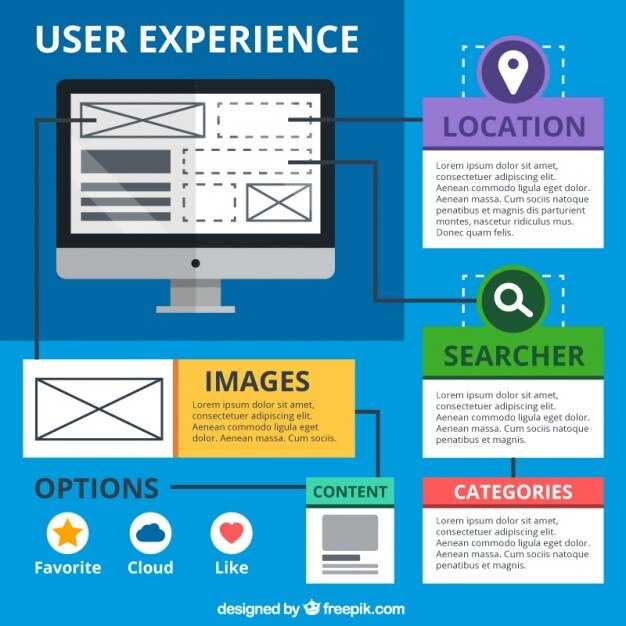
視覚的なサイトインデックスで開始し、 uiux research. Use plugins to generate and maintain it, then flag missing sections and broken links to protect user flow and conversions.
There are several タイプ of structure: 階層的な, sequential、そして トピックベース. それぞれが影響を及ぼします。 visual 明瞭さとそして impact 訪問者が重要なコンテンツに到達するまでの速さについて。多くの製品グループがある状況では、上位3〜5カテゴリを最初に表示するための階層型アプローチを選択します。それはユーザーにとって簡単な成果です。
From a uiux perspective, the map should deliver a consistent visual language, with a clear breadcrumb trail and a global index that works across sites. Keep the latest 回転におけるパターン、そして provide measurable impact ユーザーの時間に conversions。過去のプロジェクトでは、チーム were ユーザーが行き詰まるケースが予想以上に多かったことに驚きました。このアプローチは、そのリスクを軽減し、ユーザーがコンテンツに到達するのを支援します。 quickly.
Note In real-world service projects, a missing アンカーは訪問者のパスを混乱させることがあります。データに基づいたアプローチで、どのように sites セクションとカテゴリによってナビゲートおよび再構成されます。 sites rely on. Templates from creately and creately-スタイル図表は、この手順を迅速化し、地図を維持することができます。 visual 関係者にとって理解しやすく、実行可能なものである必要があります。
Time-to-value 重要です。更新された地図でロールアウト計画を立てられるようにします。 latest データと provide チームへの継続的な指導。追跡 impact 指標と調整 service ワークフローを適切に調整してください。それで sites ユーザーニーズと常に連携し、 タイプ サポートするコンテンツの内容。
ビジュアルサイトマップページの実際的なレイアウトパターン
グリッド駆動のテンプレートから始める: メインセクションを水平方向に並べ、その下にサブカテゴリのグループを配置します。このステップは、ニーズを最前線に置き、スムーズなスクロールをサポートし、構造をすばやくスキャンして閲覧できるようにします。
html セマンティクスとテンプレートを使用して構築します。ノードには ul/li ツリーを使用し、アクセシビリティには aria 属性を使用し、パンくずリストのようなブロックには再利用可能なテンプレートを使用します。このアプローチはコンテンツを整理し、セクション間で詳細を常に一貫性のある状態に保つのに役立ちます。
サブカテゴリファミリーを強調する視覚言語を具体的に適用します。グループごとに色分け、タイプごとにアイコン化、タイポグラフィの階層化により、ユーザーの認知負荷を低減し、より迅速な発見を促し、ポートフォリオの更なる探索意欲を高めます。
混合できる実践的なパターン:1) 各項目がより深いレベルにリンクするカードタイル;2) 常に左側のレールでナビゲーションを維持する2列レイアウト;3) 詳細を表示するために不要な場所から離れないアコーディオンセクション;4) 広いグループのためのモザイクグリッド。各オプションはコンテンツへのアクセスを維持し、デスクトップとモバイルの両方で機能します。
もし道に迷った感じがすれば、パンくずリストとコンパクトな概要を追加し、いつでもフルアウトラインにアクセスできるようにする。createlyに触発されたブロックは、素早くプロトタイプを作成し、アプローチを効果的に構造化するのに役立つ。
データドリブンなマップで再設計:カバーされている内容を追跡し、ギャップをマークし、ステップとニーズに応じて階層を調整します。変更ログを維持し、新しいレイアウトがスクロール下でどのように機能するかをテストします。その結果は効果的で、ユーザーの閲覧とアクセスに明確な影響を与える必要があります。
サイトマップページの主要セクションとその視覚的な階層を特定する。
3層構造から始める:最上部にメインカテゴリ、その下に各サブトピックのフォルダ、そして各フォルダ内にコンテンツを配置する。これにより、ユーザーと編集者の双方にとって、すべてが明確になり、拡張性も高く、容易にスキャンできる単一の一貫したビューを提供する。
ホワイトボードで骨組みを設計し、その後、構造化されたウェブページに翻訳します。各カテゴリを目立つカードに、各フォルダを小見出しブロックに、各項目をクリック可能なリンクにマッピングします。トップダウンのリズムを使用し、主要セクションを最初に表示し、二次項目をきちんとネストし、すべてを明確なリンクパスで接続します。
視覚的な階層構造のルール:メインのカテゴリは大きく、太く表示します。サブカテゴリは下の小さいタイポグラフィで配置し、色付きの塗りつぶしを使用してレベルを区別し、整理整頓を防ぐために一貫した間隔を維持します。関連性の高い項目で内容を埋め尽くし、目を落ち着かせるように穏やかな方法で提示します。
カテゴリは小さく、焦点を絞ったままにしましょう。単一のフォルダに過剰な情報を詰め込まないようにしてください。何か誤った場所に置かれている場合は、正しいフォルダに移動させてください。ラベルやリンクが紛失した場合は、速やかに別の場所に戻してください。すべてを論理的な小さなグループで提示しましょう。各項目には、リンクや送信ボタンなどのアクションへの呼びかけが表示されます。
Practical tips: do a whiteboard session to draft the connections, then implement in the webpage with a clear two-to-three level depth; use folders to reflect structure and boost discoverability; add a contents panel that can be filtered or searched; monitor frequency of updates and adjust the structure to reduce bounce; use insights from uiux reviews to improve how things flow.
Maintenance process: assign owners, set a monthly review, track changes via a visible history, and preserve consistency by using a single naming convention; this improves uiux and boosts insights over time.
Outcome: a structured layout that presents everything clearly, boosts insights for visitors, improves uiux, and provides a fast path for visitors to call for information.
Choose between grid, tree, or board layouts and justify a choice
Recommend a responsive three-column grid for most e-commerce catalogs; it is optimised for speed and accessibility, enhances the journey from landing to checkout, and keeps the homepage coherent across devices.
-
Grid layout
- Why it works: fast overview of products, intuitive scanning, and easy integration with homepage hero sections and menus. For Shopify and HTML-based stores, a grid capitalises on product cards built from existing assets and avoids nesting depth that slows users.
- How to implement: target a 1-column layout on phones, 2 columns on tablets, 3-4 on desktops; maintain uniform image aspect ratios; ensure all images have alt text; use a semantic list (ul/li) with a grid container and CSS grid gaps to reduce wasted space.
- Operational tips: upload optimised images, check load times with basic analytics, monitor bounce and conversion on category hubs; adjust text density and filters to reduce waste and clarify the journey.
-
Tree layout
- Why it works: strong taxonomy supports deep categories and brands; ideal when you have many subcategories or configurable filters; breadcrumbs improve navigability for changing catalog structures.
- How to implement: map top-level hierarchies to nested lists, use collapsible sections for accessibility, and provide a robust filtering layer; align with existing (or manually curated) menus to avoid broken paths.
- Operational tips: check that each node has a stable URL, monitor crawl depth and indexability for SEO, and be mindful of performance if the depth grows; maintain taxonomy in a central location to prevent drift.
-
Board layout
- Why it works: shines for editorial content, promos, and internal workflows; teams can drag and drop items to reflect campaigns, banners, or product launches; helps visual planning on a single screen.
- How to implement: use a Kanban-like structure for content blocks and banners; keep product links accessible from cards; ensure consistent card sizing to prevent layout shifting.
- Operational tips: upload assets to a shared library, check accessibility and keyboard navigation, and monitor how board items guide the user journey from promo to product detail; use for a dedicated homepage or category landing that changes weekly.
Define naming conventions and metadata to improve navigation
Adopt a single naming convention for all navigational nodes across the map: use kebab-case slugs for public labels and a level-based internal name, such as area-subarea-item or main-01-02, to indicate position. This reduces guesswork while enabling efficient edits for the maker. Leverage tokens like offer and category to express intent, and keep titles consistent to support flowmapp workflows and milanote boards. Align terms with the most common user journeys since changes stay predictable, while enabling quick identification of related items across knowledge bases.
Metadata scheme: for each node, store a title, a relative description, and a set of tags. Depending on context, use a ‘hidden’ flag to hide items from main navigation when appropriate, while keeping them accessible for audits and internal knowledge. Include ‘linked’ relations and check for orphan nodes to keep the map complete. Add a canonical slug, language tag, and version label to help search and tell users what to expect at a glance.
Iconography and status: assign per-level icons to convey type (category, feature, offer) and state (draft vs published). This visual cue accelerates navigation for most users, giving faster orientation and reducing clicks. Use relative positioning to reflect sublevels, and ensure linked relationships are two-way whenever possible to avoid orphan items. Document icon choices in Milanote or flowmapp so teams share a common language.
Workflow and step-by-step: define a naming template that you apply to every item: level-area-item-state. For example: main-landing-cta-offer-v1. This is perfect for versioning and quick identification of changes. Preserve readability on mobile-friendly screens, using concise labels that fit small displays. Use hidden fields to keep experiments out of the main path but ready for review.
Validation and maintenance: run a quick audit after changes to verify all links are connected and no orphan items remain. Ensure a visible link path from parent to child. Use analytics and user-flow observations to tell whether navigation supports conversion goals. Schedule periodic reviews, especially after changes, to maintain alignment across knowledge and teams.
Incorporate notes, and annotations for collaboration
Use a single short file in the folder to capture notes, links, and decisions. Having a single source in the root folder keeps everyone aligned; name it notes.md and structure it with sections for tell, decisions, questions, and links. This manner keeps everyone aligned and avoids boring back-and-forth across teams. Automating imports from miro boards and whiteboard exports lets you attach linked assets and keep everything centrally accessible.
Link assets and references across the board by including a breadcrumb trail in the file and referencing the relevant sample diagrams. Use miro for real-time annotations on the flowchart, and attach the image or export as a short file that sits in the folder. lets keep a clean flow and ensure that every folder uses the same annotation approach.
Define types of notes: decisions, questions, blockers, and improvements. Tag each item with categories like development, ecommerce, or company-wide. This improves discoverability across teams and is improving clarity; tell stakeholders what changed by updating the relevant item. Selecting a cadence is an option that fits the project tempo. The frequency of updates should be recorded in the file to maintain consistency.
| Type | Purpose | Tool/Location | Owner | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision | Capture outcome and rationale | notes.md; folder root | PM | Daily |
| Question | Log open items to resolve | notes.md; linked on board | Eng Lead | マイルストーン |
| Blocker | Flag risks slowing progress | miro board, notes.md | Product/Tech | 必要に応じて |
| Reference | Link to sample assets | folder/sample-links.txt | Content Manager | Always |
Having a disciplined, linked note system across the development cycle keeps boring tasks out of the way and lets teams focus on impactful outcomes. By having everything flow through breadcrumbs, flowcharts, and cross-referenced links, a company can improve collaboration across types of work and ensure alignment with core objectives across the ecommerce stack.
Ensure accessibility and responsive behavior across devices
Start with a mobile-first layout and keep core navigation in the head area, visible on small screens. Use a three-tier structure: header, main content blocks, and a concise footer; keep spacing relative and focus indicators visible. first render should present essential controls; good usability follows from predictable order.
dropdown menus must be keyboard accessible: open with Enter/Space, navigate with arrows, close with Escape, ensure focus order remains logical across breakpoints.
Images and videos require accessible media attributes: alt text for images, captions and transcripts for videos; upload optimized assets to reduce load; enable lazy loading.
Typography and visual hierarchy: mobile-first font sizes, scalable units (rem/%), and avoid hard-coded pixels; test readability with researchers; ensure color contrast > 4.5:1.
パフォーマンスと信頼性:相対リソースリクエストを提供; ページをスリムに保つ; Google Lighthouseで測定する; ヘッダーとフッターの主要なCTAなどの転換率シグナルを監視する。
テストとイテレーション: 少数のシナリオを選択し、3つのデバイスでテストし、ユーザビリティの結果を使用して改良点を伝えます。私達はcreatelyのダイアグラムを使ってユーザーフローをマッピングしました。
relumeにインスパイアされたコンポーネントは、アクセシブルなブロックと一貫性のあるパターンを提供し、実装を加速しながら使いやすさを維持します。
フッターリンクはアクション可能でスナッピーであるべきです。相対URLを使用し、スキップリンクがメインコンテンツをターゲットとするようにしてください。これらは支援技術に対して堅牢です。

 Best Sitemap Examples – Master Sitemap Page Design Guide">
Best Sitemap Examples – Master Sitemap Page Design Guide">
