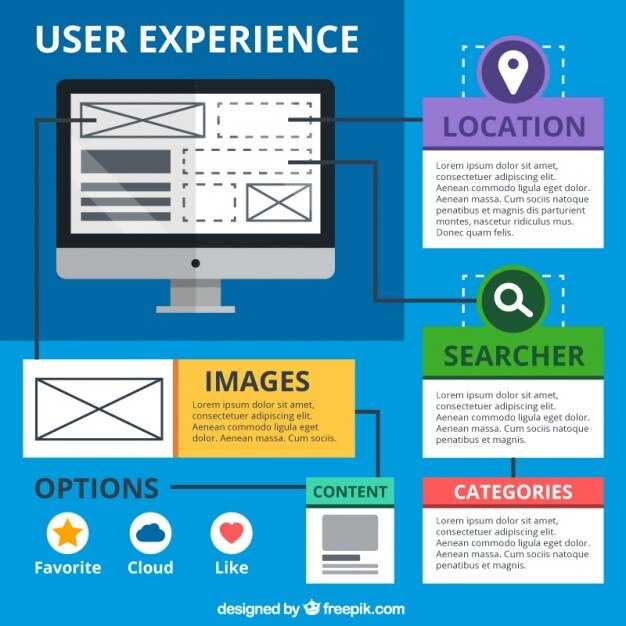
Start met een visuele site-index die uitgelijnd is met uiux onderzoek. Gebruik plugins om het te genereren en te onderhouden, en dan vlaggen Translation not available or invalid. secties en gebroken links om de gebruikersstroom te beschermen en conversions.
Er zijn verschillende types van structuur: hiërarchisch, sequentieel, en topic-based. Elke factor beïnvloedt. visueel helderheid en het impact over hoe snel bezoekers essentiële content bereiken. In een situatie met veel productgroepen, kies dan een hiërarchische aanpak om eerst de top 3–5 categorieën weer te geven; dat is snel gewonnen terrein voor gebruikers.
Van een uiux perspective, de kaart zou consistent moeten leveren visueel language, met een duidelijke breadcrumb trail en een globale index die over het geheel genomen werkt. sites. Houd het latest patronen in rotatie, en provide meetbaar impact op gebruikerstijd om conversions. In eerdere projecten, teams were verbaasd over hoeveel gebruikers in een doodlopend punt terechtkomen; deze aanpak vermindert dat risico en helpt gebruikers om content te bereiken snel.
Let op In real-world service projects, a Translation not available or invalid. een anker een bezoekerspad kan ontsporen. Gebruik een data-gedreven aanpak om te auditen hoe sites worden genavigeerd en herschikt door secties en categorieën die sites rely on. Templates from creately and creately-stijldiaprogrammen kunnen deze stap versnellen, terwijl de kaart wordt behouden visueel en bruikbaar voor stakeholders.
Time-to-value zaken; streef naar een implementatieplan dat u in staat stelt om de kaart bij te werken met latest data en provide voortdurende begeleiding naar teams. Track impact in metrics en pas aan service workflows dienovereenkomstig aanpassen, zodat sites blijf afgestemd op de behoeften van de gebruiker en types van content die u ondersteunt.
Praktische lay-outpatronen voor visuele sitemap-pagina's
Begin met een door een raster gestuurde basisstructuur: plaats hoofdonderdelen in een horizontale rij en lijnt een subcategoriegroep eronder uit. Deze stap houdt behoeften centraal, ondersteunt vloeiend scrollen en maakt de structuur direct scanbaar voor browsen.
Bouw met HTML semantiek en templates: gebruik ul/li bomen voor nodes, aria attributen voor toegankelijkheid en herbruikbare templates voor blokken die lijken op een breadcrumb. Deze aanpak helpt bij het organiseren van content en houdt details consistent over secties.
Specifiek een visuele taal toepassen die subcategorie families benadrukt: kleuren per groep, iconografie per type en typografische hiërarchie. De impact is een lagere cognitieve belasting en snellere ontdekking, wat gebruikers inspireert om meer van de portfolio te verkennen.
Praktische patronen die je kunt combineren: 1) kaarttegels waarbij elk item linkt naar een dieper niveau; 2) tweecolum lay-out met een aanhoudende linker rail voor navigatie; 3) accordeonsecties om details te onthullen zonder te verlaten; 4) mozaïekroosters voor brede groepen. Elke optie houdt de inhoud toegankelijk en werkt zowel op desktop als mobiel.
Als een pad verloren lijkt, voeg kruimels toe en een compact overzicht; geef toegang tot de volledige outline vanaf elk punt. Creately-geïnspireerde blokken helpen snel te prototypen en de aanpak effectief gestructureerd te houden.
Redesign with a data-driven map: track what is covered, mark gaps, and adjust the hierarchy by step and needs; keep a changelog, and test how the new layout performs under scrolling. The result must be effective, with clear impact on user browsing and access.
Identify core sections and their visual hierarchy for a sitemap page
Start with a three-tier structure: main categories at the top, a folder for subtopics under each, and contents inside each folder. This keeps everything clear, scalable, and easy to scan for users and editors alike, coming through a single, cohesive view.
Whiteboard the skeleton, then translate it into a structured webpage: map each category to a prominent card, each folder to a subheading block, and each item to a clickable link. Use a top-down rhythm so main sections come through first, with secondary items neatly nested, and everything connected via clear link paths.
Visual hierarchy rules: main categories should be larger and bolder; subcategories sit underneath with smaller typography; use colored fills to separate levels; maintain consistent spacing to avoid clutter. Keep contents filled with relevant items, and present things in a calm manner to guide the eye.
Categories should be kept small and focused; avoid overloading any single folder; if something doesnt belong, move it to a correct folder; if a label or link gets lost, relocate it promptly; present everything in logical small groups; each item shows a call to action, such as a link or submit button.
Practical tips: do a whiteboard session to draft the connections, then implement in the webpage with a clear two-to-three level depth; use folders to reflect structure and boost discoverability; add a contents panel that can be filtered or searched; monitor frequency of updates and adjust the structure to reduce bounce; use insights from uiux reviews to improve how things flow.
Maintenance process: assign owners, set a monthly review, track changes via a visible history, and preserve consistency by using a single naming convention; this improves uiux and boosts insights over time.
Outcome: a structured layout that presents everything clearly, boosts insights for visitors, improves uiux, and provides a fast path for visitors to call for information.
Choose between grid, tree, or board layouts and justify a choice
Recommend a responsive three-column grid for most e-commerce catalogs; it is optimised for speed and accessibility, enhances the journey from landing to checkout, and keeps the homepage coherent across devices.
-
Rasterindeling
- Why it works: fast overview of products, intuitive scanning, and easy integration with homepage hero sections and menus. For Shopify and HTML-based stores, a grid capitalises on product cards built from existing assets and avoids nesting depth that slows users.
- How to implement: target a 1-column layout on phones, 2 columns on tablets, 3-4 on desktops; maintain uniform image aspect ratios; ensure all images have alt text; use a semantic list (ul/li) with a grid container and CSS grid gaps to reduce wasted space.
- Operational tips: upload optimised images, check load times with basic analytics, monitor bounce and conversion on category hubs; adjust text density and filters to reduce waste and clarify the journey.
-
Tree layout
- Why it works: strong taxonomy supports deep categories and brands; ideal when you have many subcategories or configurable filters; breadcrumbs improve navigability for changing catalog structures.
- How to implement: map top-level hierarchies to nested lists, use collapsible sections for accessibility, and provide a robust filtering layer; align with existing (or manually curated) menus to avoid broken paths.
- Operational tips: check that each node has a stable URL, monitor crawl depth and indexability for SEO, and be mindful of performance if the depth grows; maintain taxonomy in a central location to prevent drift.
-
Board layout
- Why it works: shines for editorial content, promos, and internal workflows; teams can drag and drop items to reflect campaigns, banners, or product launches; helps visual planning on a single screen.
- How to implement: use a Kanban-like structure for content blocks and banners; keep product links accessible from cards; ensure consistent card sizing to prevent layout shifting.
- Operational tips: upload assets to a shared library, check accessibility and keyboard navigation, and monitor how board items guide the user journey from promo to product detail; use for a dedicated homepage or category landing that changes weekly.
Define naming conventions and metadata to improve navigation
Adopt a single naming convention for all navigational nodes across the map: use kebab-case slugs for public labels and a level-based internal name, such as area-subarea-item or main-01-02, to indicate position. This reduces guesswork while enabling efficient edits for the maker. Leverage tokens like offer and category to express intent, and keep titles consistent to support flowmapp workflows and milanote boards. Align terms with the most common user journeys since changes stay predictable, while enabling quick identification of related items across knowledge bases.
Metadata scheme: for each node, store a title, a relative description, and a set of tags. Depending on context, use a ‘hidden’ flag to hide items from main navigation when appropriate, while keeping them accessible for audits and internal knowledge. Include ‘linked’ relations and check for orphan nodes to keep the map complete. Add a canonical slug, language tag, and version label to help search and tell users what to expect at a glance.
Iconography and status: assign per-level icons to convey type (category, feature, offer) and state (draft vs published). This visual cue accelerates navigation for most users, giving faster orientation and reducing clicks. Use relative positioning to reflect sublevels, and ensure linked relationships are two-way whenever possible to avoid orphan items. Document icon choices in Milanote or flowmapp so teams share a common language.
Workflow and step-by-step: define a naming template that you apply to every item: level-area-item-state. For example: main-landing-cta-offer-v1. This is perfect for versioning and quick identification of changes. Preserve readability on mobile-friendly screens, using concise labels that fit small displays. Use hidden fields to keep experiments out of the main path but ready for review.
Validation and maintenance: run a quick audit after changes to verify all links are connected and no orphan items remain. Ensure a visible link path from parent to child. Use analytics and user-flow observations to tell whether navigation supports conversion goals. Schedule periodic reviews, especially after changes, to maintain alignment across knowledge and teams.
Incorporate notes, and annotations for collaboration
Use a single short file in the folder to capture notes, links, and decisions. Having a single source in the root folder keeps everyone aligned; name it notes.md and structure it with sections for tell, decisions, questions, and links. This manner keeps everyone aligned and avoids boring back-and-forth across teams. Automating imports from miro boards and whiteboard exports lets you attach linked assets and keep everything centrally accessible.
Link assets and references across the board by including a breadcrumb trail in the file and referencing the relevant sample diagrams. Use miro for real-time annotations on the flowchart, and attach the image or export as a short file that sits in the folder. lets keep a clean flow and ensure that every folder uses the same annotation approach.
Define types of notes: decisions, questions, blockers, and improvements. Tag each item with categories like development, ecommerce, or company-wide. This improves discoverability across teams and is improving clarity; tell stakeholders what changed by updating the relevant item. Selecting a cadence is an option that fits the project tempo. The frequency of updates should be recorded in the file to maintain consistency.
| Type | Purpose | Tool/Location | Owner | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beslissing | Capture outcome and rationale | notes.md; folder root | PM | Daily |
| Question | Log open items to resolve | notes.md; linked on board | Eng Lead | Milestones |
| Blocker | Flag risks slowing progress | miro board, notes.md | Product/Tech | Naar behoefte |
| Reference | Link to sample assets | folder/sample-links.txt | Content Manager | Always |
Een gedisciplineerd, verbonden notatiesysteem gedurende de ontwikkelcyclus houdt saaie taken uit de weg en stelt teams in staat zich te concentreren op impactvolle resultaten. Door ervoor te zorgen dat alles via kruimels, flowcharts en kruisverwijzingen verloopt, kan een bedrijf de samenwerking tussen verschillende soorten werk verbeteren en de afstemming met de kernobjectieven binnen de e-commerce stack waarborgen.
Zorg voor toegankelijkheid en responsief gedrag op alle apparaten
Begin met een mobile-first layout en houd de kernnavigatie in het hoofdbereik, zichtbaar op kleine schermen. Gebruik een drielaagse structuur: header, inhoudsblokken en een beknopte footer; houd de spacing relatief en focusindicatoren zichtbaar. De eerste weergave moet essentiële besturingselementen presenteren; goede bruikbaarheid volgt uit een voorspelbare volgorde.
dropdownmenu's moeten via het toetsenbord toegankelijk zijn: openen met Enter/Spatie, navigeren met pijltjestoetsen, sluiten met Escape, zorg ervoor dat de focusvolgorde logisch blijft over breakpoint heen.
Afbeeldingen en video's vereisen toegankelijke media-attributen: alt-tekst voor afbeeldingen, ondertitels en transcripten voor video's; upload geoptimaliseerde assets om de belasting te verminderen; schakel lazy loading in.
Typografie en visuele hiërarchie: mobiel-eerst lettergroottes, schaalbare eenheden (rem/%), en vermijd hard-gecodeerde pixels; test leesbaarheid met onderzoekers; zorg voor kleurrecontrast > 4.5:1.
Performance en authenticiteit: bedien relatieve resourceverzoeken; houd pagina's slank; meet met Google Lighthouse; monitor conversiesignalen zoals primaire CTA's in de header en footer.
Testen en iteratie: kies een kleine set scenario's, test op drie apparaten en gebruik bruikbaarheidresultaten om verfijningen te vertellen; we hebben creately diagrammen gebruikt om gebruikersstromen in kaart te brengen.
Relume-geïnspireerde componenten leveren toegankelijke blokken en consistente patronen, waardoor de implementatie wordt versneld terwijl de bruikbaarheid behouden blijft.
Footer links moeten actiegericht en beknopt zijn; gebruik relatieve URL's en zorg ervoor dat skip links de hoofdinhoud bereiken; ze zijn robuust voor assistive tech.

 Best Sitemap Voorbeelden – Master Sitemap Pagina Ontwerpgids">
Best Sitemap Voorbeelden – Master Sitemap Pagina Ontwerpgids">
