Recommendation: Start with a lean interface that ships clean code, organizes pages into focused dashboards, and emphasizes accessibility and descriptive stats. Employ adminone patterns and adminty tokens to achieve consistency, while a moment of data collection drives detailed visualization and flexible functions.
Each pick emphasizes modular components, sharp visualization surfaces, and responsive pages that scale from mobile to desktop. Youd explore code-splitting strategies, stats panels, and a consistent interface grammar that reduces cognitive load while preserving functions.
Expect scrolling patterns to be deliberate rather than endless; the set prioritizes accessibility, keyboard friendly controls, and processes that samla data while never overwhelming users. The aim is to let youd map stats och functions to real tasks within a compact interface.
In practice, balance between visualization and concise data blocks shines. A strong emphasis on visualization helps youd interpret stats at a glance, while blocks with drill-down charts keep teams aligned. With a lightweight codebase, pages stay nimble and adaptable, supporting accessibility och scrolling patterns that stay readable. Honest data with transparent visuals avoid lies from misinterpretation.
The catalog of ten signals a disciplined mjukvara approach: a common adminone logic, a concise set of functions, a clear path to collect data, and attention to accessibility. Youd never lose track of where to touch controls, while adminty-ready themes offer flexibility without sacrificing consistency.
Assess responsive behavior across devices with fluid grids and breakpoint tests
Start with a fluid grid using CSS grid: twelve columns with minmax(0, 1fr) tracks, and containers that scale with the viewport. This yields nine readable tiles on wide viewports and gracefully stacks to a single column on narrow screens, delivering a clean, great-looking experience that never breaks layout on some devices. It gives developers a first solid base to navigate across choices in density, while remaining predictable on any device; matt can specifically review looks across tiers to ensure consistency. This approach also reduces tons of guesswork in layout decisions.
Practical steps
Apply smooth transitions using animatecss so moves between breakpoints stay predictable; dropdowns anchor with popperjs; predesigned components from dashio and adminlte allows fast composition of panels, cards, and forms. Use googles or material cues in nextjs to keep visuals cohesive. Across nine sizes, specifically track layout shifts, wrapping, and click targets; this gives the developer actionable insights to improve experience.
Measurement tips
Create a lightweight test harness run in a browser, with emulation covering common devices; this approach helps you manage functionalities across breakpoints and meets the need of reliable behavior; export results to a sheet, note container widths, grid gaps, and typography scale via clamp(). Ensure mobile keyboard interactions remain accessible and click targets stay visible when panels collapse. youd tweak container max-widths, grid definitions, and breakpoint values until the looks stay clean across all sizes, then ship.
Evaluate included UI components: cards, tables, forms, and widgets
Pick cards that present core tasks and answer questions at a glance; ensure visuals support staff workflows and quick decisions; reuse the same theme tokens across pages to maintain professionalism; test across vertical sites to ensure consistency; googles-style filters on cards speed up queries; about hierarchy, users see the most important data first; there must be clear contrast and readable typography.
Cards and visual density
Cards should be compact with a strong header, concise body, and actionable footer; include an icon, a short metric, and a CTA; ensure they adapt when the screen narrows; check alignment, padding, and the ability to reuse the same card across sites; this reflects professionalism and supports quick scanning.
Tables, forms, and widgets integration
Tables provide sorting, filtering, and pagination; ensure headers stay visible on scroll and numeric columns align; enable exporting to CSV; incorporate responsive breakpoints so readability remains across levels; pricing sections should show levels side by side, enabling a quick select of options; forms must include accessible labeling, inline validation, and keyboard navigation; widgets should be modular, fetch data via APIs, and present time-based metrics that can be rearranged within a single theme; this covers user needs with concise, cohesive UI across sites.
Check data visualization options: native SVG charts, Chart.js, and D3 support
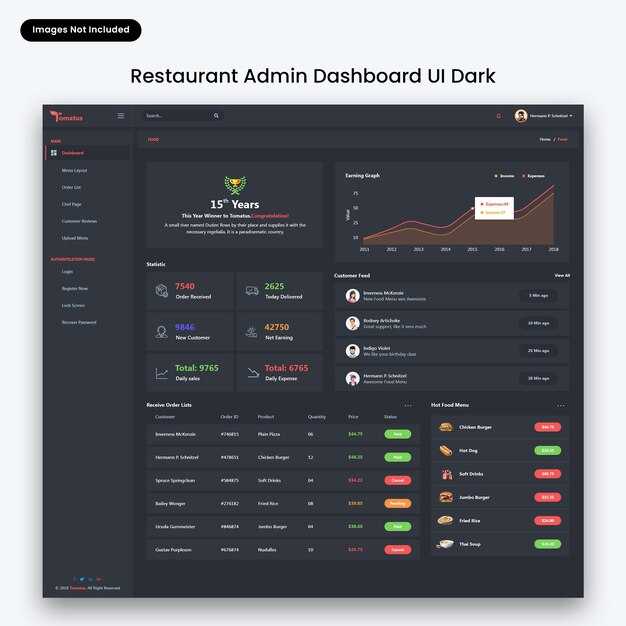
Recommendation: Start with native SVG charts to maximize performance while keeping loading light. Inline SVGs render within your platform color tokens, and charts scale across the range without extra dependencies. This setup stands in both small and large projects, supports editing details on cards in full-width interfaces, and lends a rich, clear visual baseline for rapid launch. There, a thoughtful investment pays off as your data grows and your team expands. shaan notes this path is worth pursuing when you want a quick, light alternative that scales with your needs.
Native SVG charts: fast, accessible, and easily themed
SVG-based charts offer full control over appearance and interaction. There is no dependency bloat, and you can wire them into the flowbite-enabled interface. They remain helpful for editing details in cards and keep performance high as data grows. Understanding how data maps to visuals helps you plan colors, scales, and transitions. In staradmin-inspired layouts, SVG charts blend with light, full-width sections, preserving a clean interface and swiftly loading.
Chart.js vs D3: trade-offs and use cases
Chart.js provides a swift setup with a polished set of charts that cover common needs. It comes with sensible defaults and fits well in a platform that uses color tokens across the range. It is worth using when you want quick, consistent visuals across your projects. The learning curve is gentle, and the integration with your interface remains strong. D3 offers rich, bespoke visuals and granular control over interactions, transitions, and data structure. If your understanding of data storytelling demands nuance, D3 is the alternative that pays off over time. The investment in learning D3 can take your visual storytelling to a new level, enabling a full-width display that stands out in any light theme.
Test accessibility and keyboard navigation for all widgets and controls
Perform a vast keyboard-first audit across blocks and widgets, including inputs, buttons, sliders, menus, and editors such as quilljs, addressing a variety of selection controls. Having a plan that prioritizes non-visual navigation helps hospital-grade interfaces remain usable by everyone, including assistive technologies and keyboard users.
Apply skip navigation at the top of pages, ensure a visible focus ring, and modify CSS to preserve focus outlines across themes. Use a simple focus strategy: tab through elements in a logical sequence, then confirm that each control shows a clear focus indicator. Enough contrast on focus states matters for readability in bright environments.
Test non-text controls to ensure accessible naming: give each control an aria-label or aria-labelledby equivalent; ensure groups with toggles, checkboxes, and radios expose meaningful names. When using dynamic widgets, ensure live regions announce changes when the user interacts with selections or blocks of content, and confirm a consistent selection focus path.
In rich editors like quilljs, ensure all toolbar items are reachable with Tab; ensure internal dropdowns, popovers, and modals trap focus as needed; provide a way to close with Escape and return focus to the triggering element.
Practical steps you can apply today
Add visible focus indicators first, then verify keyboard navigation on each widget and control block. Publish a simple, repeatable checklist and use it as a baseline in QA cycles. Include a minimal test suite that covers modal dialogs, menus, date pickers, and the editor toolbar. Nalika’s team suggests scanning a vast set of pages, then expanding coverage to a broader selection of blocks and functionalities, quickly.
Tools and resources
Leverage open-source scanners such as axe-core and Lighthouse to identify contrast, focus, and naming issues. These tools are free to use and integrate into CI; you can download a compact checklist as a gist and adapt it across projects. The gist can guide direction, fonts, and style decisions, ensuring compatibility across systems and websites. This approach yields better accessibility outcomes across different fonts and color schemes, making benefits visible in user cohorts with diverse needs.
Meddelanden och samarbete: för enkelt register över ändringar som påverkar tangentbordsnavigering och tillgänglighet. En väldokumenterad ändringslogg hjälper team att justera inställningar, modifiera komponenter och upprätthålla konsekvens när nya widgetar eller funktioner introduceras i det stora gränssnittet. Nalikas engagemang säkerställer en praktisk sjukhusanpassad strategi på verkliga webbplatser.
Anpassningsvägar, granskning: struktur, CSS och tillgångsorganisation
Rekommendation: Börja med en enda källa till sanning: root tokens i CSS-variabler och ett modulärt, komponentdrivet CSS-system som exponerar ett litet öppet API via data-attribut. Det här tillvägagångssättet gör att dussintals kort, paneler och widgets känns sammanhållna, samtidigt som det möjliggör omfattande anpassning utan att röra strukturell markering. För hantering av tillgångar, behåll standardfonter och -ikoner under en dedikerad tillgångscentral och använd förbyggda mönster för att snabba upp integreringen och underlätta underhållet. Även om det tillför initialt arbete, är utdelningen skalbara, smidiga upplevelser över freedash-gränssnitt och en långsiktigare väg med ökade investeringar.
Struktur och CSS-organisation
- Kataloglayout: assets/icons, assets/fonts, assets/images; css/base/root.css; css/components; css/layouts; css/themes; plus komponentmappar som components/cards, components/panels, components/widgets. Denna struktur är byggd för att vara skalbar och stödja dussintals element med minimal friktion.
- Namngivningsregler: kebab-case för klasser och ett BEM-liknande schema (till exempel .card–compact, .panel__header). Detta håller stilarna läsbara och enkla att utöka när uppsättningen växer.
- Tokenstrategi: definiera färger, mellanrum och radier som CSS-anpassade egenskaper i :root och per-temaväljare; detta ökar flexibiliteten och möjliggör smidig temaväxling. En förbyggd palett kan läggas till för att framhäva förstklassig rikedom över teman.
- Tillgänglighet och prestanda: använd minimala selektorer, undvik tunga skuggor i standardlägen, aktivera lättviktiga övergångar på paneler och säkerställ tillräcklig färgkontrast så att alla widgetar förblir användbara i alla teman.
Temanpassning och tillgångspipeline
- Temanpassning: implementera CSS-variabler som –color-bg, –color-text, –color-accent, –radius; byt tema genom att växla en klass på rotelementet; detta tillvägagångssätt är skalbart och stöder enkelt dussintals paletter.
- Tillgångsorganisation: centralisera typsnitt och ikoner under tillgångar; föredra lokalt hostade typsnitt, och håll bilder slimmade; Googles CDN kan undvikas genom att hosta tillgångar lokalt för att minska latens; detta håller tillgångsladdningen jämn och förutsägbar.
- Plugin-metod: designa ett minimalt plugin-API så att du kan lägga till widgets eller paneler utan att bryta grundläggande tokens och struktur; i freedash-installationer utökar detta bara kapaciteten samtidigt som det bevarar konsekvensen och underlättar underhållet.
- Dokumentation och introduktion: skriv sammanfattande guider, inklusive en snabbstartssektion; inkludera exempel som visar hur man åsidosätter färger, lägger till nya widgets och utökar med plugins; dessa höjdpunkter hjälper utvecklare att tänka på investeringar i framtida iterationer och undvika drift.

 10 Best HTML Dashboard Template Examples for 2025">
10 Best HTML Dashboard Template Examples for 2025">
